Mac OS Setup
This guide explains how to set up your Mac OS / Linux environment to run Shesha applications locally, including both the backend (.NET) and frontend (React.js), with Microsoft SQL Server running in Docker.
Tools You Need
- Git – Required for accessing code from git-based version control systems.
- Docker – Used to run Microsoft SQL Server as a containerized application.
- .NET 8 SDK & Runtime – Needed for the backend (ASP.NET Core) and for SQL-Package to work.
- Node.js 22 – Required to run the Shesha frontend (React.js).
- SQL-Package – Imports the starter database from a
.bacpacfile. - Visual Studio Code (or an AI-infused fork) – Recommended IDE for editing both frontend and backend code. (Note: Visual Studio is no longer supported on Mac OS).
- Database Client Extension on VSCode – To connect to SQL Server, browse databases, and run queries. Download extension
Tip: Some commands may require administrator privileges. In that case, prefix them with:
sudo ...
1. Download & Install Docker
Download Docker Desktop for Mac from docker.com and install it.
Once Docker is running, you can use docker commands in the terminal to create, start, stop, and manage containers.
For more details:
Quickstart: Install and connect to SQL Server in Docker
1.1 Pull SQL Server Image
docker pull --platform linux/amd64 mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
1.2 Run the Container
Once the SQL Server image is downloaded, create a container:
docker run --platform linux/amd64 -d -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" -e "MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD=@123Shesha" \
-p 1433:1433 --name SQL_Server_Docker \
mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
After running this command, SQL Server will be running in a container with the following credentials:
- User ID:
sa - Password:
@123Shesha
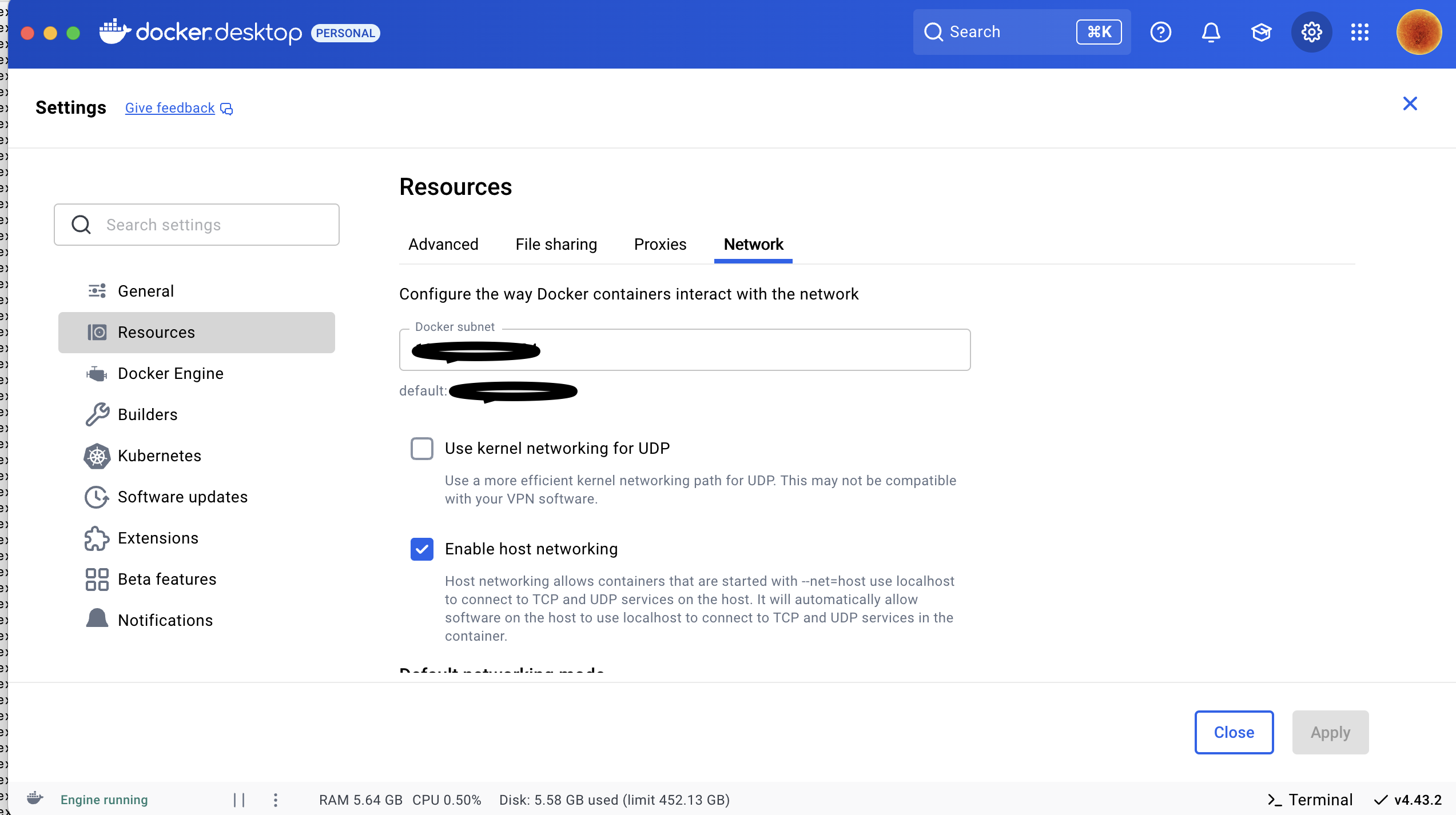
1.3 Enable Host Networking in Docker
Make sure to enable host networking in Docker Desktop so that your machine’s network calls can access the container’s network:
2. Importing the Starter Database into SQL Server
On Windows, we could use Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio's Import Data-tier Application wizard. On Mac OS, we use SQL-Package instead.
2.1 Install .NET 8
If not already installed, download the Arm64 (Apple Silicon) or x64 (Intel) version here:
.NET 8 Download
2.2 Install SQL-Package
dotnet tool install -g microsoft.sqlpackage
After installation, follow the terminal instructions to add SQL-Package to your PATH.
Close and reopen your terminal after installation.
Documentation: Install SQL-Package
2.3 Creating the Shesha Starter Project
-
Download the Shesha Starter Template, which contains:
- Adminportal – React.js frontend
- Backend – ASP.NET Core backend
- Database – Seeded SQL Server
.bacpacfile
-
Unzip the project and note the directory path.
Naming note: Replace placeholders like
ProjectNameandOrganisationNamewith the actual names you chose when generating the starter project.
2.4 Importing the Database
In the unzipped project directory, you will find a .bacpac file:
Example location:
~/Downloads/<OrganisationName.ProjectName>/<ProjectName>.bacpac
Run:
sqlpackage /Action:Import /SourceFile:"./Downloads/<OrganisationName.ProjectName>/<ProjectName>.bacpac" /TargetConnectionString:"Server=localhost,1433;Initial Catalog=ProjectName;Persist Security Info=False;User ID=sa;Password=@123Shesha;MultipleActiveResultSets=False;Encrypt=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;Connection Timeout=30;"
Once complete, use your choice of SQL Server client and verify that the ShaProjectName database exists.
3. Running the Backend
3.1 Open Backend in VS Code
Open the backend directory in your code editor.
3.2 Update Connection String
Edit:
/src/OrganisationName.ProjectName.Web.Host/appsettings.json
Replace the Default connection string:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "Server=localhost,1433;Initial Catalog=ProjectName;Persist Security Info=False;User ID=sa;Password=@123Shesha;MultipleActiveResultSets=False;Encrypt=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;Connection Timeout=30;"
}
}
3.3 Build & Run
Working directory structure:
backend
├── src
├── nupkg
├── .nuget
├── test
└── ...
Build:
dotnet build
Run:
dotnet run --project src/OrganisationName.ProjectName.Web.Host --urls "http://localhost:21021;https://localhost:44362"
SSL Note: If you do not have a local development certificate, install and trust it:
dotnet dev-certs https --trust
4. Running the Frontend
Go to the adminportal directory:
cd adminportal
npm install
npm run dev
The frontend should now be running locally and connected to your backend.